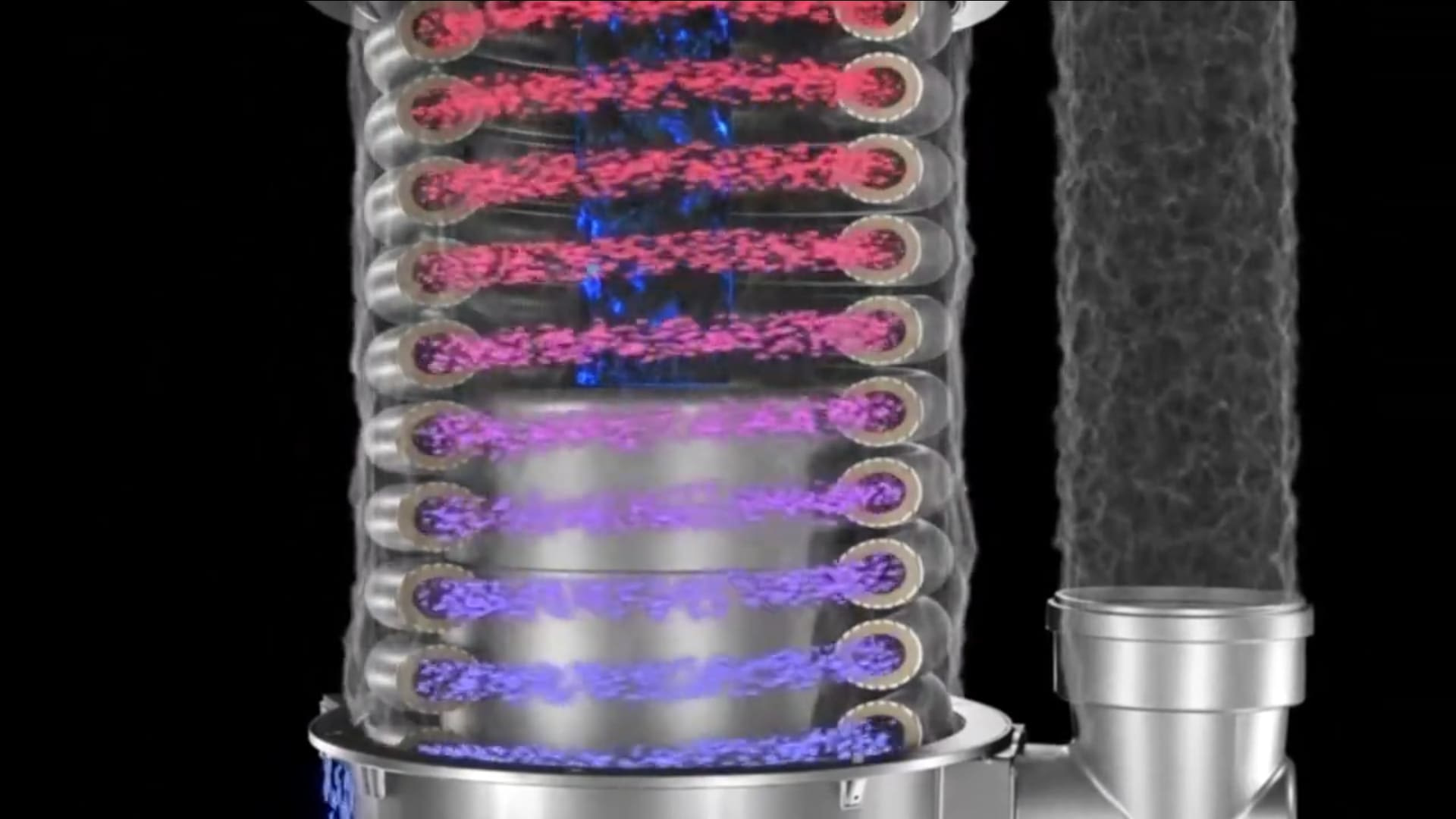
Condensing tankless water heaters are more energy efficient compared to non-condensing tankless water heaters as they utilize the heat from the exhaust gas to preheat the incoming cold water. This results in cooler exhaust gas and higher energy efficiency.
Exploring The Basics
When it comes to tankless water heaters, the main topic of discussion is condensing vs non-condensing models. Condensing tankless water heaters are more energy efficient, utilizing the heat from exhaust gas to preheat incoming cold water, while non-condensing models do not.
This makes condensing tankless water heaters a better choice for increased energy savings.
Understanding Tankless Water Heater Technology
Tankless water heaters have become a popular choice for homeowners looking for energy-efficient and space-saving alternatives to traditional storage tank water heaters. Unlike conventional units that store and continuously heat water, tankless water heaters heat water on demand, providing a constant supply of hot water whenever it is needed.
But how do tankless water heaters actually work? Understanding the technology behind them is crucial to making an informed decision when choosing between condensing and non-condensing options.
At the core of a tankless water heater is the heat exchanger, which is responsible for heating the water. In non-condensing tankless models, the heat exchanger is made of copper or stainless steel and operates at a high temperature. As the water passes through the heat exchanger, it is quickly heated to the desired temperature and then delivered to the faucets or appliances.
Tip: Non-condensing tankless water heaters are more suitable for areas with mild climates where the incoming water temperature is relatively warm.
Key Differences Between Condensing And Non-condensing Heaters
When it comes to tankless water heaters, there are two main types: condensing and non-condensing. The key difference lies in how they handle the exhaust gases produced during the combustion process.
Condensing tankless water heaters
Condensing tankless water heaters have an additional heat exchanger that utilizes the heat from the exhaust gases to preheat the cold water before it enters the main heat exchanger. This not only increases the overall efficiency of the unit but also results in cooler exhaust gases that can be vented through PVC pipes.
One of the major advantages of condensing tankless water heaters is their higher energy efficiency. By utilizing the waste heat from the exhaust gases, they are able to extract more heat from the fuel, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
However, it’s important to note that condensing tankless water heaters are generally more expensive than non-condensing models due to the additional heat exchanger and advanced technology they incorporate.
Non-condensing tankless water heaters
Non-condensing tankless water heaters, on the other hand, do not utilize the heat from the exhaust gases. Instead, they rely solely on the main heat exchanger to heat the water. This means that the exhaust gases from non-condensing units are hotter and require a metal venting system to safely remove them from the house.
Non-condensing tankless water heaters are typically less expensive than their condensing counterparts, making them a popular choice in areas where the incoming water temperature is relatively high or in situations where cost is a major factor.
Energy Efficiency: Initial Context
When comparing condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters, energy efficiency is a crucial factor to consider. By choosing an energy-efficient model, you can not only reduce your carbon footprint but also save money on your energy bills in the long run.
Keep in mind that the energy efficiency of a tankless water heater is measured in terms of its Energy Factor (EF). Higher EF values indicate better energy efficiency, meaning the unit can convert a higher percentage of energy input into usable hot water.
Next, we will explore the energy efficiency of condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters in more detail.
Functionality Dissected
Understanding the inner workings of tankless water heaters is essential when deciding which type is best suited for your needs. In this section, we will dissect the functionality of condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters, shedding light on their distinct features and energy transfer processes.
How Condensing Tankless Water Heaters Operate
Condensing tankless water heaters are designed with an additional heat exchanger, which separates them from their non-condensing counterparts. This heat exchanger takes advantage of the hot exhaust gas produced during the combustion process, utilizing it to preheat the incoming cold water.
Unlike non-condensing tankless water heaters, which exhaust hot gases directly through a vent, condensing models have cooler exhaust gases due to the heat transfer process. This not only makes them more energy-efficient but also allows for a unique venting system.
Non-condensing Counterparts: Operation Highlights
Non-condensing tankless water heaters, although lacking the additional heat exchanger found in condensing models, are still effective at providing hot water on demand. These units rely solely on heating elements to heat water as it flows through the unit.
Unlike their condensing counterparts, non-condensing tankless water heaters use a more straightforward venting system. They either utilize indoor air for combustion and vent the exhaust outside (known as power-vent), or they pull in air from the outside and have separate intake and exhaust vents (known as direct-vent).
While non-condensing tankless water heaters may not have the same energy efficiency as condensing models, they still offer a reliable and efficient solution for hot water needs.
Comparing The Energy Transfer Processes
When it comes to energy transfer, condensing tankless water heaters have the upper hand due to their additional heat exchanger. This component allows them to extract heat from the exhaust gas and use it to preheat the cold water before it reaches the main heating elements.
In contrast, non-condensing tankless water heaters rely solely on their heating elements to raise the temperature of the water as it flows through. While they may not extract heat from the exhaust gases, they still provide fast and efficient hot water delivery.
To summarize, while condensing tankless water heaters offer superior energy efficiency and a unique venting system, non-condensing models provide a reliable and efficient solution without the need for an additional heat exchanger. Your decision ultimately depends on your specific hot water needs and priorities.
Installation And Maintenance
When it comes to installation and maintenance of condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters, the key difference lies in their efficiency. Condensing tankless water heaters utilize an additional heat exchanger to preheat cold water, making them more energy efficient and producing cooler exhaust gas.
On the other hand, non-condensing tankless water heaters do not have this feature.
Installation Complexities Of Each Type
When it comes to installing tankless water heaters, there are some crucial differences between condensing and non-condensing models. Non-condensing tankless water heaters are relatively straightforward to install, requiring a direct vent or power vent system to safely exhaust the combustion gases. On the other hand, condensing tankless water heaters require a more complex installation process due to the additional heat exchanger.
The installation of condensing tankless water heaters involves creating a condensate drain line to safely dispose of the acidic condensate created during the heating process. This drain line needs to be properly installed and connected to a drain point, which adds an additional step to the installation process.
Moreover, condensing tankless water heaters also tend to have larger dimensions compared to non-condensing models. This can make the installation process more challenging, especially in spaces where there is limited room.
Long-term Maintenance Comparison
When it comes to long-term maintenance, condensing tankless water heaters have an advantage over non-condensing models. The additional heat exchanger in condensing tankless water heaters helps to increase energy efficiency by utilizing the heat from exhaust gases. However, this also means that condensing models are more prone to accumulating mineral deposits and sediments.
Regular maintenance is crucial for both types of tankless water heaters. Non-condensing models require periodic flushing to remove mineral buildup, which can affect performance and efficiency. On the other hand, condensing tankless water heaters require not only flushing but also regular inspection and cleaning of the condensate drain line to prevent clogs and ensure proper functioning.
It is important to note that the maintenance requirements of both types of tankless water heaters can vary depending on the water quality and usage patterns in your area. Consulting the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations is essential to ensure proper long-term maintenance.
Durability Outlook For Condensing Vs Non-condensing
When it comes to durability, both condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters are designed to provide long-lasting performance. However, there are a few factors to consider that may impact the durability outlook for each type.
Condensing tankless water heaters, with their additional components such as the heat exchanger and condensate drain line, may have a slightly higher chance of experiencing issues related to these components. Ensuring regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent any problems and ensure the long-term durability of condensing models.
On the other hand, non-condensing tankless water heaters, while simpler in design, can still experience wear and tear over time. Flushing to remove mineral deposits and periodic inspections to check for any potential issues are recommended to maintain their performance and longevity.
In summary, both condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters can provide durable and efficient performance with proper installation and maintenance. Understanding the installation complexities, long-term maintenance requirements, and maintenance best practices for each type will help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Cost And Savings Analysis
When considering a tankless water heater for your home, it’s important to analyze the cost and potential savings associated with different types of models. In this section, we will compare the initial purchase and installation costs, long-term energy savings potential, and analyze the return on investment (ROI) for condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters.
Initial Purchase And Installation Costs
One of the first factors to consider when comparing condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters is the initial purchase and installation costs. The cost of a condensing tankless water heater is typically higher than that of a non-condensing model. This can be attributed to the additional components and technology required for condensing units to capture and utilize exhaust gas heat.
Additionally, installation costs may vary depending on the complexity of the project. While both condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters require professional installation, condensing units may require additional venting or modifications to accommodate the exhaust gas heat recovery system.
Overall, the initial purchase and installation costs of a condensing tankless water heater are generally higher compared to a non-condensing model.
Long-term Energy Savings Potential
Despite the higher initial costs, condensing tankless water heaters offer significant long-term energy savings potential. The main reason for this is the utilization of exhaust gas heat in condensing units. The extra heat exchanger in condensing tankless water heaters captures heat from the exhaust gas and uses it to preheat the incoming cold water. This process increases energy efficiency and reduces energy consumption compared to non-condensing models.
In addition, condensing tankless water heaters have cooler exhaust gas to vent, further reducing energy losses. This lower exhaust gas temperature also allows for the use of PVC venting, which is less expensive and easier to install compared to metal venting required for non-condensing units.
The long-term energy savings potential of a condensing tankless water heater is significantly higher compared to a non-condensing model, making it a more cost-effective choice over time.
Analyzing Roi: Condensing Vs Non-condensing Tankless Water Heater
To determine the return on investment (ROI) for a condensing or non-condensing tankless water heater, it’s essential to consider the initial purchase and installation costs, as well as the long-term energy savings potential.
Although the initial costs of a condensing tankless water heater are higher, the long-term energy savings can offset this difference and provide a higher ROI over the lifespan of the unit. With lower energy consumption, homeowners can expect reduced monthly utility bills and potential rebates or incentives for choosing an energy-efficient model.
On the other hand, non-condensing tankless water heaters may have lower upfront costs, but higher energy consumption and less efficiency, leading to higher energy bills in the long run.
Overall, when analyzing the ROI, it becomes clear that the energy savings potential of a condensing tankless water heater outweighs the initial purchase and installation costs, making it a more financially viable choice in the long term.
Environmental Impact Considerations
When it comes to choosing a tankless water heater, considering the environmental impact is crucial. Two key factors to consider are emissions and environmental footprint, as well as assessing the ecological benefits of each system. Let’s dive into the details to determine which option is greener and explore overall environmental considerations.
Emissions And Environmental Footprint
One of the primary concerns when comparing condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters is their emissions and environmental footprint. Condensing tankless water heaters have an advantage in this regard. These units utilize an additional heat exchanger to extract heat from the exhaust gas and preheat the inflowing cold water. As a result, condensing units are more energy-efficient and produce cooler exhaust gas to vent. This means lower emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants.
Assessing The Ecological Benefits Of Each System
When assessing the ecological benefits of condensing vs. non-condensing tankless water heaters, it is essential to consider energy consumption and resource utilization. Condensing units have higher efficiency due to their ability to recover heat from the exhaust gas. This means reduced energy consumption and lower demand for natural resources. On the other hand, non-condensing tankless water heaters may consume more energy to achieve the desired water temperature, leading to higher overall energy consumption.
Which Is Greener? Overall Environmental Considerations
Considering the overall environmental impact, condensing tankless water heaters emerge as the greener choice. Their higher efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced resource consumption contribute to a smaller ecological footprint. Additionally, the energy savings achieved with condensing units can result in long-term cost savings for homeowners.
In conclusion, when it comes to choosing between condensing and non-condensing tankless water heaters, making an environmentally conscious decision is paramount. The additional heat exchanger in condensing units makes them more energy efficient, resulting in lower emissions and a reduced environmental footprint. By considering these factors, homeowners can make a greener choice that benefits both the planet and their wallets.

Credit: www.angi.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Condensing Vs Non Condensing Tankless Water Heater
Is A Condensing Tankless Water Heater Better Than Non Condensing?
Condensing tankless water heaters are better than non-condensing heaters because they are more energy efficient. They use a heat exchanger to preheat the cold water with the exhaust gas, resulting in cooler exhaust and lower energy consumption.
What Is The Difference Between Condensing And Non Condensing Efficiency?
Condensing tankless water heaters are more energy efficient because they use an extra heat exchanger to preheat the inflowing cold water with the exhaust gas. This results in cooler exhaust gas and improved efficiency. Non-condensing tankless water heaters do not have this extra heat exchanger.
How Do You Vent A Non Condensing Tankless Water Heater?
To vent a non-condensing tankless water heater, you can choose between power-venting or direct-venting. Power-vented units use indoor air for combustion and vent the exhaust outside. Direct-vented units pull in air from outside and have separate intake and exhaust vents.
This allows for safe and efficient venting of the heater.
What Does Non Condensing Mean?
Non-condensing means that humidity is present, but it doesn’t cause condensation to form. It is a type of testing where a humidity and temperature cycle is performed without the formation of condensation.
Conclusion
The choice between a condensing and non-condensing tankless water heater comes down to energy efficiency. Condensing units utilize a heat exchanger to recycle heat from the exhaust gas, resulting in higher energy efficiency and cooler exhaust gas. On the other hand, non-condensing units do not utilize this feature.
Ultimately, if you’re looking for a more energy-efficient and eco-friendly option, a condensing tankless water heater is the way to go. Consider your specific needs and weigh the benefits before making a decision.

I am a Water Heater specialist writer and blogger based in the USA & UK. I have been working with Water Heater for six long years. And I give trips on various Water Heater problems and solutions. I have a lot of experience with Water Heater And I share them here